Know Your Most Fertile Days with Precision
Our advanced ovulation calculator helps you track your cycle, predict your fertile window, and maximize your chances of conception.

Ovulation Calculator
Enter your last period date and cycle length to calculate your fertile window, ovulation date, and more.
How Our Ovulation Calculator Works
Understanding your menstrual cycle is key to tracking your fertility. Our calculator uses proven medical science to predict your most fertile days.
Enter Your Cycle Data
Input the first day of your last period and your average cycle length. If you don't know your cycle length, the calculator will use the average of 28 days.
Advanced Calculations
Our algorithm calculates your estimated ovulation date (typically 14 days before your next period) and identifies your 6-day fertile window when pregnancy is possible.
Get Personalized Results
View your fertile window, ovulation date, next period, and even estimated due date if conception occurs. All results include detailed explanations.
The Science Behind Our Calculator
Our ovulation calculator is based on the following scientific principles:
Luteal Phase Consistency
While the follicular phase can vary, the luteal phase (from ovulation to next period) is consistently around 14 days for most women.
Fertile Window
Sperm can survive up to 5 days in a woman's reproductive tract, and an egg lives for about 24 hours after ovulation, creating a 6-day window when pregnancy is possible.
Peak Fertility
The 3 days leading up to and including ovulation day are when you're most likely to conceive.
Cycle Variations
Our calculator accounts for different cycle lengths, adjusting predictions accordingly.
Note: While our calculator provides accurate estimates based on cycle averages, every woman's body is unique. For the most precise tracking, consider combining our calculator with other fertility awareness methods like basal body temperature tracking and monitoring cervical mucus changes.
Essential Fertility Facts
Understanding your fertility is empowering. Here's what you need to know about your menstrual cycle and conception.
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
Follicular Phase
This phase begins on the first day of your period and ends with ovulation. During this time, follicles in your ovaries develop and estrogen levels rise, preparing for the release of an egg.
Ovulation
Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary, pushed down the fallopian tube, and is available to be fertilized. This typically happens around day 14 of a 28-day cycle.
Luteal Phase
After ovulation, the follicle that released the egg transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This phase lasts about 14 days and ends with your period if pregnancy doesn't occur.
Signs of Ovulation
Cervical Mucus Changes
As you approach ovulation, your cervical mucus becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy (similar to egg whites), which helps sperm travel to the egg.
Basal Body Temperature Rise
Your basal body temperature rises slightly (0.2-0.5°F) after ovulation due to increased progesterone. Tracking this change can help confirm ovulation has occurred.
Other Physical Signs
Some women experience mild pelvic pain (mittelschmerz), increased sex drive, light spotting, breast tenderness, or heightened sense of smell around ovulation.
Factors Affecting Fertility
- •Age: Female fertility gradually declines with age, especially after 35.
- •Weight: Being significantly underweight or overweight can disrupt hormone balance and ovulation.
- •Stress: High stress levels can affect hormone production and potentially delay or prevent ovulation.
- •Exercise: Moderate exercise supports fertility, but excessive exercise can interfere with ovulation.
- •Smoking and Alcohol: Both can reduce fertility and the chances of conception.
Tips for Conception
- •Time Intercourse: Have sex every 1-2 days during your fertile window, especially the 3 days leading up to and including ovulation.
- •Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise moderately, and maintain a healthy weight.
- •Take Prenatal Vitamins: Start taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid at least 3 months before trying to conceive.
- •Limit Caffeine: Reduce caffeine intake to less than 200mg per day (about one 12oz cup of coffee).
- •Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness.
When to Seek Help
If you've been trying to conceive without success, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider:
Under 35
If you've been trying for 12 months without success
35-40 Years
If you've been trying for 6 months without success
Over 40
If you've been trying for 3 months without success
A fertility specialist can help identify any underlying issues and discuss treatment options to help you achieve pregnancy. Don't hesitate to seek professional guidance if you have concerns about your fertility.
Understanding Fertilization
Watch this educational video to learn about the fascinating process of fertilization and how conception occurs.
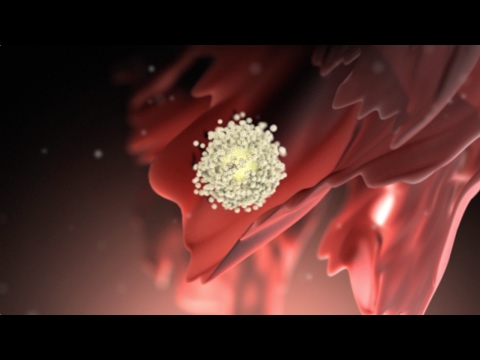
Watch on YouTube
Fertilization
Nucleus Medical Media
83M views
About This Video
This educational animation by Nucleus Medical Media illustrates the process of fertilization - when sperm meets egg. Understanding this process is crucial for anyone trying to conceive, as it shows exactly what happens during the most critical moment of conception.
The video demonstrates how sperm travel through the female reproductive tract, the challenges they face, and the cellular changes that occur when fertilization is successful. This knowledge complements our ovulation calculator by showing what happens during your fertile window.
Signs to Expect Throughout Your Cycle
Understanding the physical signs your body displays can help you identify different phases of your menstrual cycle.
Bloating
Many women experience bloating before and during their period due to hormonal changes that cause water retention.
Mucus Changes
Cervical mucus becomes clear, slippery and stretchy (like egg whites) during your fertile window, helping sperm travel to the egg.
Cramps
Mild cramping or one-sided pain (mittelschmerz) can occur during ovulation as the egg is released from the ovary.
Sore Breasts
Breast tenderness or sensitivity is common before your period and can also be an early sign of pregnancy.
Mood Changes
Hormonal fluctuations throughout your cycle can affect your mood, causing irritability, anxiety, or emotional sensitivity.
Basal Temperature Rise
Your basal body temperature rises slightly (0.2-0.5°F) after ovulation due to increased progesterone levels.
Tracking Your Body's Signals
Your body provides valuable clues about your fertility throughout your menstrual cycle. By tracking these signs, you can better understand your body's patterns and identify your most fertile days.
Fertility Awareness Methods
Combining multiple tracking methods—such as basal body temperature, cervical mucus observations, and cycle tracking—provides the most accurate picture of your fertility.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you notice unusual symptoms or significant changes in your cycle, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider. This includes very heavy bleeding, severe pain, or cycles that suddenly become irregular.
Remember that every woman's body is unique, and what's normal for one person may not be for another. Regular tracking helps you establish your personal baseline and notice any changes that might need attention.
Success Stories
Thousands of women have used our ovulation calculator to help them on their fertility journey.
Jessica M.
Age 32, California
"After 6 months of trying with no success, I started using this ovulation calculator. Within 2 months of tracking my cycle and timing intercourse during my fertile window, I got pregnant! The detailed explanations helped me understand my body better."
Amanda T.
Age 28, Texas
"I have irregular cycles, which made it hard to predict ovulation. This calculator helped me identify patterns I hadn't noticed before. The expandable cards with detailed information were so educational. I'm now expecting my first baby!"
Sarah R.
Age 35, New York
"As someone over 35, I was worried about my fertility. This calculator helped me understand my cycle better and identify my most fertile days. The educational content about factors affecting fertility was eye-opening. We conceived after 4 months!"
"Ovulation Calculator has helped thousands of women understand their fertility and achieve pregnancy. While individual results may vary, our calculator provides accurate, science-based predictions to maximize your chances of conception."
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to common questions about ovulation, fertility, and conception.
Our ovulation calculator provides estimates based on the average menstrual cycle. It's most accurate for women with regular cycles. The calculator assumes ovulation occurs 14 days before the next period, which is true for most women. However, individual variations exist, and factors like stress, illness, or hormonal imbalances can affect ovulation timing. For the most accurate tracking, combine our calculator with other methods like basal body temperature tracking and ovulation predictor kits.
Yes, you can use our calculator with irregular periods, but the predictions may be less accurate. The calculator works best when you can provide an average cycle length. If your cycles vary significantly, consider tracking for several months to determine your average cycle length. For irregular cycles, we recommend combining our calculator with other fertility awareness methods for more accurate predictions.
The best time to have sex when trying to conceive is during your fertile window, particularly the 3 days leading up to and including ovulation day. Sperm can survive up to 5 days in a woman's reproductive tract, while an egg lives for only about 24 hours after ovulation. Having intercourse every 1-2 days during your fertile window maximizes your chances of conception. Remember that the day of ovulation and the day before have the highest pregnancy rates.
For the most accurate results, it's best to wait until the day after your missed period to take a pregnancy test. This gives your body enough time to produce detectable levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), the pregnancy hormone that pregnancy tests detect. Taking a test too early might result in a false negative. If your period is late and you get a negative result, wait a few days and test again. For the highest accuracy, use first morning urine, which contains the highest concentration of hCG.
Yes, stress can significantly impact ovulation and fertility. Chronic stress can disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls the release of stress hormones like cortisol. These hormones can interfere with the reproductive hormones needed for ovulation. Severe stress may delay or even prevent ovulation in some cycles. Additionally, stress can affect libido and sexual frequency, further reducing conception chances. Stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, adequate sleep, and regular exercise may help support normal ovulation and improve fertility.
The time it takes to conceive varies widely among couples. For healthy couples in their 20s or early 30s with no fertility issues, about 25% conceive in the first month of trying, 60% within 6 months, and 80-90% within one year. Factors affecting conception time include age, frequency of intercourse, timing of intercourse relative to ovulation, overall health, and any underlying fertility issues. If you're under 35 and haven't conceived after a year of trying, or over 35 and haven't conceived after 6 months, consider consulting a healthcare provider.
While it's unlikely, it is possible to get pregnant if you have sex during your period, especially if you have a shorter menstrual cycle. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to 5 days. If you have a short cycle and ovulate early (for example, on day 10), sperm from intercourse during the end of your period could still be present when you ovulate. Additionally, some women experience breakthrough bleeding or spotting around ovulation, which might be mistaken for a period. If you're trying to avoid pregnancy, it's safest to use contraception throughout your cycle.
To increase your chances of conception: 1) Track your fertile window and have regular intercourse during this time, 2) Maintain a healthy weight - both underweight and overweight can affect fertility, 3) Take prenatal vitamins with folic acid, 4) Avoid smoking, excessive alcohol, and recreational drugs, 5) Limit caffeine to 200mg daily, 6) Manage stress through relaxation techniques, 7) Get regular moderate exercise, 8) Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, 9) Avoid excessive heat exposure for men (hot tubs, saunas), and 10) Consider a preconception checkup with your healthcare provider to address any health concerns.
Still Have Questions?
Our comprehensive ovulation calculator is designed to help you understand your fertility cycle, but we understand you might have specific questions about your situation.
For personalized advice regarding your fertility, we recommend consulting with a healthcare provider or reproductive specialist who can provide guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Take Control of Your Fertility Journey Today
Our free ovulation calculator helps you identify your most fertile days with precision, putting you in control of your reproductive health.
Accurate Predictions
Based on scientific research and your unique cycle data
Easy to Use
Simple interface with detailed, educational results
100% Private
Your fertility data stays private and secure
Ovulation Calculator is designed to help you understand your fertility cycle. While our calculator provides accurate estimates based on scientific principles, individual cycles may vary. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice.
Additional Resources
Popular Searches
Related Topics
Last updated: May 15, 2025 • Content medically reviewed by fertility specialists